A linked list is a linear data structure, in which the elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations.
The elements in a linked list are linked using pointers as shown in the below image:
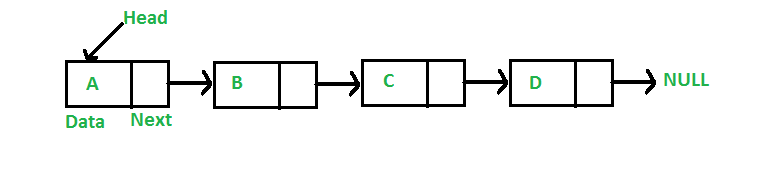
Credit to GeeksforGeeks
Types of linked list
Singly Linked List
The linked list we talked above is singly linked list.
Doubly linked list
A Doubly Linked List (DLL) contains an extra pointer, typically called previous pointer, together with next pointer and data which are there in singly linked list.
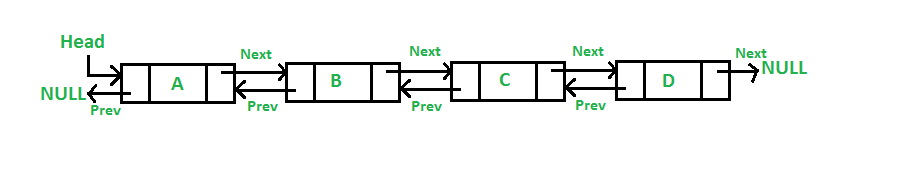
Credit to GeeksforGeeks
Circular linked list
Circular linked list is a linked list where all nodes are connected to form a circle. There is no NULL at the end. A circular linked list can be a singly circular linked list or doubly circular linked list.

Credit to GeeksforGeeks
Linked list applications
Delete a node
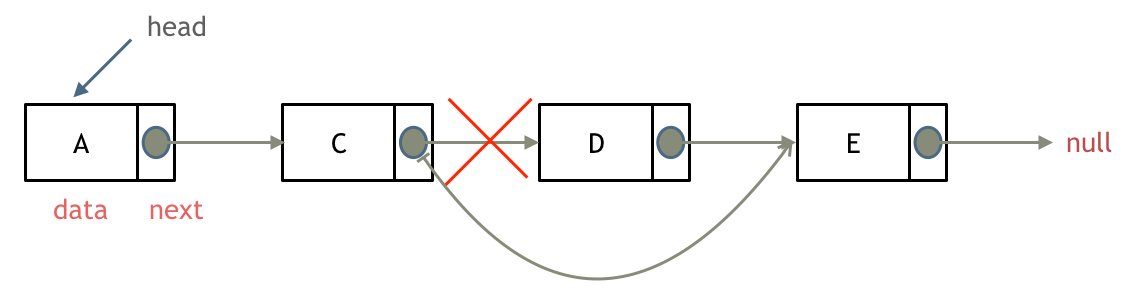
Credit to programmercarl
If we need to delete node d, what we need to do is to delete the pointer that points to node d
Add a node
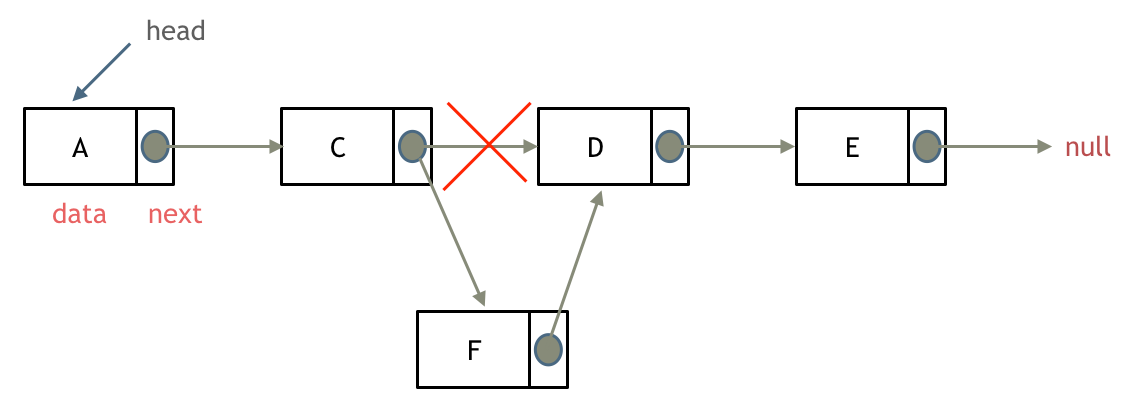
Credit to programmercarl
Add and delete both have time complexity O(1).
Note: If we need to delete the last node, we need to start from head node to the fourth node, time complexity is O(n).
Compare with list
| Add/Delete(Time Complexity) | Search(Time Complexity) | When to use | |
|---|---|---|---|
| List | O(n) | O(1) | Fixed number of data, frequently search, rarely add/delete |
| Linked List | O(1) | O(n) | Number of data various, frequently add/delete, rarely search |